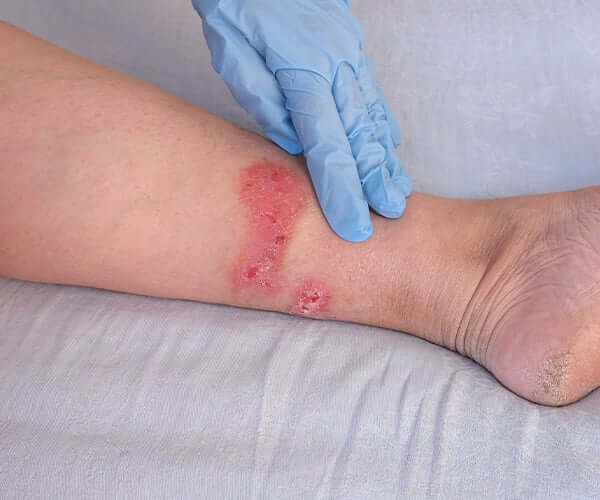
Soft tissue infections are frequently encountered medical issues that can vary in severity from mild to serious. These infections may affect the skin, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and various other connective tissues. When caused by bacteria, they need quick and effective treatment to avoid complications like abscess formation. The spread of infection, or even systemic illness. Levofloxacin is a strong fluoroquinolone antibiotic commonly used to treat various bacterial soft tissue infections because of its wide-ranging effectiveness and impressive ability to penetrate tissues. visit at Medzsupplier.
This blog will delve into Levofloxacin’s role in treating soft tissue infections. Examining how it works? Right dosing, possible side effects, and important considerations for its application.
Infections of Soft Tissue
Soft tissue infections can arise from various pathogens, with bacteria being the most frequent offenders. Notably, gram-positive organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are often responsible. These infections can appear in various forms, such as:
Cellulitis:
A bacterial infection affecting the deeper layers of the skin and the tissues beneath. Typically marked by redness, swelling, warmth, and discomfort.
Abscesses:
Collections of pus that form in tissues, organs, or cavities within the body, usually as a result of a bacterial infection.
Necrotizing Fasciitis:
An aggressive infection that quickly damages muscles, fat, and skin tissue. This condition is commonly known as “flesh-eating” disease and demands immediate medical care.
Diabetic foot infections are frequently seen in people with diabetes. These infections can impact the skin, soft tissues, and occasionally the bone, resulting in severe complications if not addressed quickly.
The Role of Levofloxacin in Managing Soft Tissue Infections
Levofloxacin is an antibiotic that works against many types of bacteria, including those often linked to soft tissue infections. The way it works includes blocking bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are essential enzymes for DNA replication, repair, and transcription in bacteria. Levofloxacin disrupts these processes, stopping bacteria from growing and spreading, which helps in effectively treating the infection. Visit the Levofloxacin Supplier
Levofloxacin is especially effective for treating soft tissue infections due to its remarkable ability to penetrate tissues. This feature enables the antibiotic to attain elevated levels in the infected tissues. Enhancing its effectiveness in eliminating the bacteria causing the infection.
Levofloxacin Dosage and Administration for Soft Tissue Infections
The dosage of Levofloxacin for treating soft tissue infections varies based on the severity of the infection and the overall health of the patient. For uncomplicated soft tissue infections, take an oral dosage of 500 mg once daily for 7 to 10 days. In more severe cases, or when other factors like diabetes or immune suppression complicate the infection. Healthcare provider might recommend a higher dose of LQuin 750 mg once daily, and they could extend the treatment duration.
Levofloxacin comes in both oral and intravenous forms, offering options for treatment. Patients experiencing severe infections that require hospitalization can start intravenous Levofloxacin and then transition to oral therapy as their condition improves.
Recognize that patients with kidney issues might need an adjustment in their Levofloxacin dosage. As the kidneys primarily eliminate the drug. A healthcare provider will assess the patient’s kidney function to decide on the right dosage.
Advantages of Levofloxacin in Treating Soft Tissue Infections
Levofloxacin provides multiple benefits for the treatment of soft tissue infections:
Comprehensive Effectiveness:
Levofloxacin effectively targets both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Making it an excellent option for treating mixed bacterial infections or when the specific pathogen remains unidentified.
Outstanding Tissue Penetration:
Levofloxacin’s capacity to achieve elevated levels in soft tissues allows it to effectively focus on the infection site. Resulting in quicker and more thorough elimination of the bacteria.
Easy Dosing:
The once-daily dosing schedule of Levofloxacin makes treatment easier for patients. Enhancing adherence and facilitating the completion of the entire therapy course.
Flexibility:
Levofloxacin is available in both oral and intravenous forms. Making it easy to transition from hospital to outpatient care and minimizing the need for extended hospital stays.
Possible Side Effects of Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is usually well-tolerated, but it can come with certain potential side effects. Some typical side effects are gastrointestinal issues like nausea, diarrhea, and stomach pain. The side effects are usually mild and tend to go away on their own.
Nonetheless, while uncommon, more significant side effects may arise. These could consist of:
Tendonitis and Tendon Rupture:
Levofloxacin increases the risk of tendon damage, particularly in older adults, people with kidney problems, and those taking corticosteroids. The Achilles tendon often gets impacted, but other tendons can also be affected. Patients should discontinue Levofloxacin and consult a healthcare professional if they notice any tendon pain, swelling, or inflammation.
Peripheral Neuropathy:
Levofloxacin can result in nerve damage, which may manifest as tingling, numbness, or weakness in the limbs. It’s crucial to inform a healthcare provider right away if you notice any symptoms, as this condition may be irreversible in certain situations.
QT Prolongation:
Levofloxacin may influence the electrical activity of the heart, resulting in an irregular heart rhythm referred to as QT prolongation. This condition can pose serious risks, particularly for individuals with existing heart issues or those on medications that influence heart rhythm.
Diarrhea Associated with Clostridium edificial:
Like many antibiotics, Levofloxacin can disturb the natural balance of bacteria in the gut. Which may result in an overgrowth of Clostridium difficile, a bacterium responsible for causing severe diarrhea.
Proper Use of Levofloxacin
Given the possibility of significant side effects and the risk of developing antibiotic resistance. It is essential to use Levofloxacin with caution. Levofloxacin should be prescribed solely when it is essential and when the advantages surpass the potential risks. It is not appropriate for use in viral infections or other situations where antibiotics are unnecessary.
Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions when taking Levofloxacin, ensuring they complete the entire course of treatment, even if they begin to feel better before finishing the medication. This approach guarantees that the infection is completely eliminated and minimizes the chances of creating antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
In summary
Levofloxacin is a strong and adaptable antibiotic that is essential in treating soft tissue infections. Its wide-ranging effectiveness, impressive tissue absorption, and easy dosing make it a strong choice for treating bacterial infections in the skin and soft tissues. Nonetheless, because of the possibility of significant side effects and the threat of antibiotic resistance. Levofloxacin must be used carefully and solely with the advice of a healthcare professional.
For patients dealing with soft tissue infections, receiving prompt and suitable treatment with Levofloxacin can result in quick recovery and help avoid complications. If you think you might have a soft tissue infection. It’s crucial to get medical help quickly to ensure you receive the right care.