Cabergoline is a medication that has gained prominence for its effectiveness in treating various medical conditions, particularly those related to hormone imbalances. Understanding the appropriate dosage and timing of Cabergoline is crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential side effects. This comprehensive guide delves into the optimal timing for taking Cabergoline, focusing on the commonly prescribed dosages of Cabergoline 0.5 mg and Cabergoline 0.25 mg. Whether you are prescribed Cabergoline for Parkinson’s disease, hyperprolactinemia, or another condition, this article aims to provide valuable insights to help you manage your treatment effectively.
What is Cabergoline?
Cabergoline is a dopamine agonist, a class of medications that mimic the action of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a significant role in regulating movement, mood, and various hormonal processes. By stimulating dopamine receptors, Cabergoline can influence these processes, making it an effective treatment for conditions where dopamine activity is deficient or dysregulated.
Medical Uses of Cabergoline
Cabergoline is primarily prescribed for the following conditions:
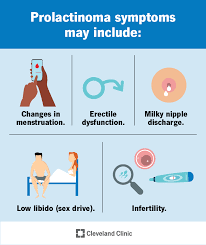
- Hyperprolactinemia: Elevated levels of prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, can lead to various symptoms such as irregular menstrual periods in women, erectile dysfunction in men, and unwanted milk production (galactorrhea) in both sexes. Cabergoline helps reduce prolactin levels, thereby alleviating these symptoms.
- Parkinson’s Disease: In Parkinson’s disease, the death of dopamine-producing neurons leads to motor symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). Cabergoline can help manage these symptoms by stimulating dopamine receptors.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Cabergoline is sometimes used off-label to treat RLS, a condition characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, typically accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
- Other Uses: Cabergoline may also be prescribed for certain pituitary tumors or other conditions as determined by a healthcare provider.
Understanding Cabergoline Dosages: 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg
Cabergoline is available in tablet form, with the most common dosages being 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg. The appropriate dosage depends on the condition being treated, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s response to the medication. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and not to adjust it without consulting a healthcare professional.
0.5 mg Dosage
The 0.5 mg dosage is typically prescribed for more severe cases or when a higher dose is necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. For instance:
- Parkinson’s Disease: Higher doses may be required to manage motor symptoms effectively.
- Severe Hyperprolactinemia: When prolactin levels are significantly elevated, a 0.5 mg dosage may be necessary to reduce prolactin to normal levels.
0.25 mg Dosage
The 0.25 mg dosage is often used for milder cases or as a starting dose to assess the patient’s tolerance to the medication. It may be sufficient for:
- Mild Hyperprolactinemia: When prolactin levels are only slightly elevated, a lower dose may effectively manage symptoms.
- Adjunct Therapy: In some cases, a lower dose may be combined with other treatments for enhanced efficacy.
The Importance of Timing in Cabergoline Administration
The timing of medication administration can significantly impact its effectiveness and the occurrence of side effects. For Cabergoline, aligning the dosage timing with the body’s natural rhythms and the pharmacokinetics of the drug can optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Pharmacokinetics of Cabergoline
Understanding how Cabergoline is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body helps in determining the best time to take it:
- Absorption: Cabergoline is well-absorbed when taken orally, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1 to 3 hours after ingestion.
- Half-Life: It has a long half-life, ranging from 63 to 109 hours, allowing for once or twice-daily dosing.
- Metabolism and Excretion: Cabergoline is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily via the kidneys.
Aligning with Natural Rhythms
Taking Cabergoline at a time that aligns with the body’s natural dopamine rhythms can enhance its effectiveness. Dopamine levels fluctuate throughout the day, and timing the medication to complement these fluctuations can help in managing symptoms more effectively.
Best Time to Take Cabergoline: Morning vs. Evening
The optimal time to take Cabergoline can vary based on individual responses and the specific condition being treated. However, there are general guidelines that can help determine whether to take it in the morning or evening.
Morning Administration
Advantages:
- Consistency with Dopamine Peaks: Dopamine levels are naturally higher in the morning, which can synergize with Cabergoline’s mechanism of action, enhancing its effectiveness.
- Minimizing Side Effects: Taking Cabergoline in the morning can help manage potential side effects like dizziness or fatigue during the day when activity levels are higher.
- Compliance: Incorporating the medication into the morning routine can improve adherence to the prescribed regimen.
Considerations:
- Morning Nausea: Some individuals may experience nausea upon waking, and taking Cabergoline with breakfast can help mitigate this side effect.
- Interaction with Other Morning Medications: If other medications are part of the morning routine, it’s essential to consider potential interactions.
Evening Administration
Advantages:
- Sleep-Related Benefits: For conditions like Restless Legs Syndrome, taking Cabergoline in the evening can help manage symptoms that typically worsen at night.
- Reduced Daytime Side Effects: Some side effects, such as dizziness or hypotension, may be less disruptive if they occur in the evening.
- Flexibility: Evening dosing can be more convenient for individuals with busy mornings.
Considerations:
- Sleep Disturbances: Although rare, some individuals may experience insomnia or restlessness if Cabergoline is taken too close to bedtime.
- Consistency: Ensuring that the evening dose is taken at the same time each day is crucial for maintaining stable drug levels.
Personalized Timing: Morning or Evening?
The decision to take Cabergoline in the morning or evening should be individualized based on:
- Response to Medication: Monitoring how the body responds to Cabergoline can inform the best time for administration. Some may find morning dosing more effective, while others may benefit from evening doses.
- Lifestyle and Routine: Aligning medication timing with daily routines can improve adherence and effectiveness.
- Side Effect Profile: Observing when side effects occur can guide whether to adjust the timing to minimize their impact.
Recommended Dosage Timing for 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg
0.5 mg Dosage
For those prescribed a 0.5 mg dosage of cabergoline, the timing can be critical to managing more severe symptoms effectively.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Typically, the 0.5 mg dose is divided into two administrations per day, often taken in the morning and early afternoon. This division helps maintain stable dopamine receptor stimulation throughout the day, managing motor symptoms more effectively.
- Hyperprolactinemia: A 0.5 mg dose may be taken once daily, preferably in the morning. Taking it with food can reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
0.25 mg Dosage
For the 0.25 mg dosage, timing may vary based on whether it is used as a starting dose or for less severe conditions:
- Starting Dose: When beginning Cabergoline therapy, a lower dose of 0.25 mg may be taken once daily, often in the morning. This allows the body to adjust to the medication, reducing the likelihood of side effects.
- Maintenance Dose: For maintenance therapy, the timing can be similar to the 0.5 mg dose, either once or twice daily, depending on the patient’s needs and the healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Factors Influencing Cabergoline Timing
Several factors can influence the optimal timing for taking Cabergoline:
Individual Metabolism
Metabolic rates vary among individuals, affecting how quickly Cabergoline is absorbed and processed. Those with faster metabolism may require more frequent dosing, while slower metabolizers might maintain therapeutic levels with less frequent administration.
Concurrent Medications
Cabergoline can interact with other medications, potentially altering its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. It’s essential to consider the timing of other medications to avoid adverse interactions. For instance, antihypertensive drugs may enhance Cabergoline’s blood pressure-lowering effects, necessitating careful timing to prevent hypotension.
Meal Timing
Taking Cabergoline with food can reduce gastrointestinal side effects like nausea. However, high-fat meals may affect the absorption rate. It’s generally recommended to take Cabergoline with a light meal unless directed otherwise by a healthcare provider.
Sleep Patterns
For individuals with conditions that affect sleep, such as Restless Legs Syndrome, taking Cabergoline in the evening may provide symptom relief during nighttime hours. Conversely, if Cabergoline causes insomnia, taking it earlier in the day can help mitigate this effect.
Activity Levels
Aligning Cabergoline dosing with periods of higher activity can optimize symptom management. For example, taking the medication before engaging in activities that require alertness and motor control can enhance its therapeutic benefits.
Practical Tips for Optimizing Cabergoline Timing
To maximize the benefits of cabergoline and minimize side effects, consider the following practical tips:
- Establish a Routine: Take cabergoline at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels and improve adherence.
- Monitor Side Effects: Pay attention to any side effects and discuss them with your healthcare provider. Adjusting the timing may alleviate certain adverse effects.
- Use Reminders: Set alarms or use a medication tracker to ensure timely intake, especially if taking multiple doses per day.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Always discuss any changes in timing or dosage with your healthcare provider before making adjustments.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water when taking cabergoline to support kidney function and reduce the risk of hypotension.
- Avoid Sudden Position Changes: To prevent dizziness or fainting, rise slowly from sitting or lying positions, especially when starting Cabergoline or adjusting the dosage timing.
Potential Side Effects and Timing Considerations
Understanding the potential side effects of Cabergoline is essential for determining the best time to take the medication.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea: Often occurs when starting treatment or increasing the dose. Taking cabergoline with food can help mitigate this effect.
- Headache: Can occur at any time; if persistent, consult a healthcare provider.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: particularly when standing up, leading to concerns about timing to minimize risks.
- Fatigue: May influence whether to take Cabergoline in the morning or evening based on when fatigue is most disruptive.
- Constipation: Taking Cabergoline with plenty of fluids and fiber can help alleviate this side effect.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Heart Valve Issues: Long-term use, especially at higher doses, has been associated with heart valve abnormalities. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential.
- Psychiatric Symptoms: Such as hallucinations or compulsive behaviors, which require immediate medical attention.
Timing to Minimize Side Effects
- Morning Dosing: Helps manage fatigue and dizziness during the day, reducing the risk of falls or accidents.
- Evening Dosing: May be preferable for those who experience insomnia or prefer to manage certain side effects overnight.
Special Considerations and Precautions
When determining the best time to take Cabergoline, certain special considerations and precautions must be kept in mind:
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Cabergoline is generally not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding unless deemed absolutely necessary by a healthcare provider. Women of childbearing age should discuss potential risks and benefits with their physician.
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Patients with a history of heart valve disease or hypertension should be closely monitored, and dosing timing may need adjustment.
- Liver or Kidney Impairment: May require dosage adjustments and careful timing to prevent accumulation of the drug.
Alcohol and Substance Use
Alcohol can exacerbate side effects like dizziness and hypotension. It’s advisable to limit or avoid alcohol while taking cabergoline.
Surgical Procedures
Inform your surgeon or dentist about Cabergoline use before any surgical procedures, as it may interact with anesthesia or other medications.
Adjusting Dosage Timing: When and How
Adjusting the timing of Cabergoline should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider. However, understanding the scenarios that may necessitate changes can help patients communicate effectively with their physicians.
Reasons to Adjust Timing
- Persistent side effects: If side effects like nausea, dizziness, or insomnia are interfering with daily life, adjusting the timing may help.
- Ineffective Symptom Control: If symptoms are not adequately managed, changing the dose schedule might enhance therapeutic effects.
- Lifestyle Changes: Shifts in daily routines, work schedules, or sleep patterns may require adjustments in medication timing.
- Concurrent Medications: Starting or stopping other medications can influence the optimal timing of Cabergoline.
How to Adjust Timing
- Gradual Changes: Small, incremental adjustments can help the body adapt without causing sudden shifts in drug levels.
- Consistent Monitoring: Keep track of symptoms and side effects when adjusting the timing to evaluate effectiveness.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Always seek professional advice before making any changes to ensure safety and efficacy.
Combining Cabergoline with Other Treatments
In some cases, Cabergoline may be part of a broader treatment regimen. Understanding how timing interacts with other treatments is essential for overall management.
Combination with Other Dopamine Agonists
Using Cabergoline alongside other dopamine agonists is uncommon and usually unnecessary. However, if required, timing must be carefully coordinated to prevent excessive dopamine stimulation and side effects.
Use with Antihypertensives
For patients taking blood pressure medications, coordinating the timing of Cabergoline can prevent additive hypotensive effects. For example, taking Cabergoline in the morning while antihypertensives are taken later can help balance blood pressure control.
Adjunctive Therapies
In treating conditions like Parkinson’s disease, Cabergoline is often used alongside other medications like levodopa. Timing must be synchronized to ensure optimal symptom management without interfering with each other’s efficacy.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
Certain lifestyle and dietary habits can influence the optimal timing and effectiveness of Cabergoline:
Meal Timing and Composition
- With Meals: Taking Cabergoline with meals can reduce gastrointestinal side effects. A light meal is generally recommended.
- High-Fat Meals: May delay absorption, potentially affecting the timing’s impact on symptom control.
- Consistency: Keeping meal times consistent with medication intake helps maintain stable drug levels.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is essential, especially since Cabergoline can cause hypotension. Drinking sufficient water throughout the day can help mitigate this risk.
Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can enhance overall well-being and may complement Cabergoline’s effects. Timing physical activity to align with medication dosing can optimize symptom management, particularly in conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
Sleep Hygiene
For those taking Cabergoline in the evening to manage nighttime symptoms, maintaining good sleep hygiene practices can enhance the benefits and reduce sleep disturbances.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring is crucial to ensuring the effectiveness and safety of Cabergoline therapy. This includes:
Clinical Assessments
Periodic evaluations by a healthcare provider to assess symptom control, side effects, and overall health status.
Laboratory Tests
Regular blood tests to monitor prolactin levels, kidney and liver function, and other relevant parameters.
Cardiac Monitoring
For long-term use, especially at higher doses, echocardiograms may be recommended to monitor heart valve function.
Patient Self-Monitoring
Keeping a symptom diary can help track how timing affects symptom control and side effects, providing valuable information for healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Cabergoline is a versatile medication with proven efficacy in treating conditions like hyperprolactinemia and Parkinson’s disease. Understanding the optimal dosage timing is essential for maximizing its therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects. Whether prescribed at 0.5 mg or 0.25 mg, aligning cabergoline intake with the body’s natural rhythms, daily routines, and individual response can significantly enhance treatment outcomes.
Morning dosing often aligns with natural dopamine peaks and can help manage daytime symptoms effectively, while evening dosing may offer benefits for nighttime conditions and reduce daytime side effects. Factors such as individual metabolism, concurrent medications, meal timing, and lifestyle must be considered when determining the best time to take cabergoline.
Ultimately, personalized medical advice from a healthcare provider is paramount. Regular monitoring and open communication with healthcare professionals will ensure that cabergoline therapy is both safe and effective, tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
By adhering to prescribed dosages, understanding the importance of timing, and being mindful of lifestyle factors, patients can effectively incorporate cabergoline into their treatment regimen, leading to improved quality of life and better management of their medical conditions.